Protect Your Skin from Sun Damage and Cancer Effectively
Exposure to the sun’s rays can bring both benefits and risks. While sunlight is essential for vitamin D synthesis, excessive exposure can lead to sun damage and even increase the risk of skin cancer. To safeguard your skin effectively, it’s vital to adopt rigorous protective measures and understand the implications of unguarded sun exposure.
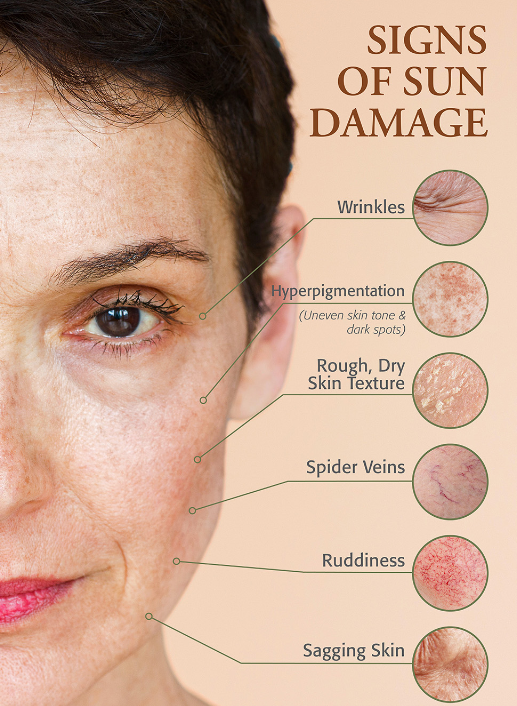
Understanding Sun Damage
Sun damage is primarily due to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. There are two types of UV radiation that impact our skin: UVA and UVB.
UVA and UVB: The Twin Perils
UVA Rays: These penetrate deep into the skin and are primarily responsible for long-term damage such as aging and wrinkles. They affect the deeper layers of the skin, potentially leading to skin cancer.
UVB Rays: These rays are responsible for sunburn and can damage the outer layers of the skin. Prolonged exposure can contribute to skin cancer as well.
Effective Sun Protection Strategies
To minimize the risk of sun damage and skin cancer, it’s crucial to implement effective sun protection strategies all year round.
Use Sunscreen Religiously
The cornerstone of sun protection is regular application of sunscreen. Choosing the right sunscreen and applying it properly can make a significant difference.
- Choose Broad-Spectrum Sunscreen: Ensure that your sunscreen offers protection against both UVA and UVB rays.
- SPF Matters: Use a sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, and apply it generously to all exposed skin.
- Reapply Frequently: Sunscreen effectiveness diminishes over time. Reapply every two hours, and more frequently if sweating or swimming.
Wear Protective Clothing
Clothing can provide a physical barrier between your skin and the sun’s harmful rays.
- Opt for Long-Sleeve Shirts and Pants: Wear clothing that covers as much skin as possible.
- Choose UPF Clothing: Some clothes are designed with an Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF). These garments offer additional protection against UV radiation.
- Don’t Forget Hats and Sunglasses: A wide-brimmed hat can protect your face, neck, and ears, while UV-blocking sunglasses can shield your eyes.
Seek Shade
Staying in the shade is one of the simplest ways to protect your skin from UV radiation.
- Avoid Peak Sun Hours: The sun’s rays are most intense between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. Plan outdoor activities outside these hours if possible.
- Utilize Umbrellas and Trees: When spending time outdoors, make use of natural or portable shade sources.
Regular Skin Checks
Early detection of skin abnormalities can be crucial in preventing skin cancer.
- Self-Examinations: Regularly check your skin for any new moles, growths, or changes in existing moles. Use mirrors to examine hard-to-see areas.
- Professional Screenings: Schedule annual check-ups with a dermatologist for a thorough skin examination.
Healthy Skincare Routine
Besides sun protection, maintaining a healthy skincare routine can aid in reducing the risk of sun damage.
Incorporate Antioxidants
Antioxidants can help repair and prevent skin damage caused by UV exposure.
- Vitamin C and E: These vitamins can neutralize free radicals produced by UV radiation, thus aiding in skin repair.
- Topical Serums: Use antioxidant-rich serums as part of your daily skincare routine for added protection.
Stay Hydrated
Hydrated skin is more resilient and better equipped to repair itself.
- Drink Plenty of Water: Ensure you consume adequate water daily to keep your skin hydrated from within.
- Moisturize Regularly: Use a quality moisturizer to maintain your skin’s moisture barrier, especially after sun exposure.
Myths and Facts about Sun Exposure
There are many misconceptions about sun exposure and sun protection. Understanding the facts can help you take the right steps to protect your skin.
Myth: Sunscreen Is Only for Sunny Days
Fact: UV rays penetrate through clouds, making it essential to wear sunscreen even on overcast days.
Myth: Darker Skin Needs Less Sun Protection
Fact: While darker skin has more melanin, which provides some protection, it is still susceptible to sun damage and skin cancer.
Myth: A Higher SPF Means You Can Stay in the Sun Longer
Fact: Higher SPF provides more protection but doesn’t extend the safe time one can spend in the sun. Reapplication is still necessary.
Protecting Vulnerable Groups
Certain groups are more vulnerable to sun damage and need extra precautions.
Children
Children’s skin is more sensitive to UV radiation. Ensure they are appropriately protected with sunscreen, clothing, and hats.
Seniors
Aging skin is more prone to damage. Seniors should take extra care to avoid excessive sun exposure and conduct regular skin checks.
Effective sun protection is a year-round commitment. By understanding the impacts of UV radiation and implementing comprehensive protective measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of sun damage and skin cancer. Make sun safety a habit, and enjoy the outdoors without compromising your skin’s health.