Menopause brings a myriad of changes to a woman’s body, some visible and others more subtle. One aspect that often goes unnoticed is its impact on oral health. The hormonal shifts during menopause can lead to significant effects on teeth and gums, necessitating increased attention to dental care. Understanding these changes can help manage and mitigate the dental challenges that may arise during this stage of life.
Hormonal Changes During Menopause
Menopause is characterized by a decline in estrogen levels, and this hormonal transformation affects multiple physiological systems, including the oral environment. The decrease in estrogen can influence blood flow to the gums, reduce bone density, and affect saliva production, which collectively have a profound impact on oral health.
Reduced Estrogen and Blood Flow
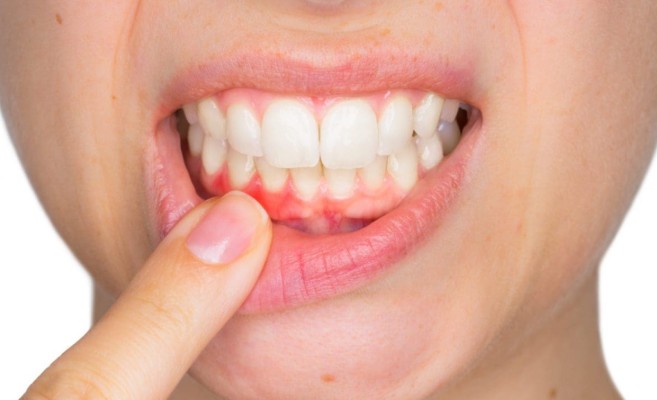
Estrogen helps maintain optimal blood circulation throughout the body. As estrogen levels drop, reduced blood flow to the gums can occur, which may lead to gum sensitivity and inflammation. This makes menopausal women more susceptible to conditions such as gingivitis and periodontitis, both of which require proactive dental hygiene and regular check-ups with a dental professional.
Impact on Saliva Production
Saliva is crucial for neutralizing acids in the mouth, washing away food particles, and safeguarding against infections. During menopause, women often experience a decrease in saliva production, leading to dry mouth or xerostomia.
Consequences of Dry Mouth
A lack of adequate saliva in the mouth can result in:
Increased risk of tooth decay: Without saliva’s protective barrier, the teeth are more exposed to harmful bacteria and acids.
Difficulty swallowing and speaking: Saliva aids in these everyday functions, and its absence can make them more challenging.
Altered taste sensations: Dry mouth can influence how foods and drinks taste.
Tips for Managing Dry Mouth
To combat dry mouth, consider the following:
- Stay hydrated: Ensure regular water intake to keep the mouth moist.
- Use moisturizing mouthwash: Seek alcohol-free options specifically designed to combat dry mouth.
- Chew sugar-free gum: This can stimulate saliva production and offer relief from dryness.
- Discuss medication changes with your doctor: Certain medications can exacerbate dry mouth symptoms; adjustments might be necessary.
Bone Loss and Dental Health
The decline in estrogen during menopause can also contribute to bone loss, affecting jawbone density. This can have significant repercussions for dental health:
Risks Associated with Bone Loss
- Loose teeth: As jawbone density decreases, the stability of teeth may be compromised, leading to looseness or shifting.
- Tooth loss: Severe bone loss can result in tooth loss if not addressed in a timely manner.
- Increased risk of fractures: Just like other bones in the body, the jawbone can become more prone to fractures with decreased density.
Strategies for Maintaining Bone Health
To support bone health during menopause:
- Consume adequate calcium and Vitamin D: Essential for bone maintenance, these nutrients can help mitigate bone density loss.
- Engage in weight-bearing exercises: Such activities promote bone strength and preservation.
- Regular dental check-ups: Routine visits allow for early detection and intervention of any changes in oral health.
Gum Health Challenges
Hormonal changes during menopause contribute to changes in gum tissue, leading to a handful of potential issues:
Common Gum Concerns
- Gingivitis and Periodontitis: As mentioned earlier, reduced blood flow and changes in oral bacteria levels contribute to these gum diseases. Symptoms include red, swollen, and bleeding gums.
- Burning Mouth Syndrome: Some women may experience a burning sensation in the mouth, often linked to hormonal shifts.
Recommendations for Gum Health
- Maintain a rigorous oral hygiene routine: Brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily are key.
- Regular dental visits: Professional cleanings are vital for managing and preventing gum issues.
- Healthy lifestyle choices: Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption, both of which can exacerbate gum problems.
Practical Steps for Improved Menopausal Dental Health
Adapting to the changes that menopause brings requires a proactive approach. Here are some actionable steps to ensure sustained dental health:
Nutrition and Lifestyle Adjustments
- Balanced diet: Incorporate foods rich in calcium, Vitamin D, and phosphorus to support both general and oral health.
- Stay hydrated: As previously noted, hydration is crucial for managing symptoms like dry mouth.
- Limit sugar intake: Excessive sugar can increase the risk of cavities, especially in the absence of sufficient saliva.
Consultation with Healthcare Professionals
- Collaborate with your dentist: Keeping your dentist informed about menopause-related changes can aid in more personalized care.
- Consult a doctor or endocrinologist: They can offer insights and treatments for managing bone density and hormone-related conditions.
Menopause is a natural phase in a woman’s life, and while it presents its own set of challenges, many oral health issues can be managed effectively with awareness and preventive care. By understanding the implications of hormonal changes on dental health, women can take informed steps to maintain their smile for years to come. Stay proactive, seek regular dental consultations, and prioritize your oral health as you navigate this significant life transition.