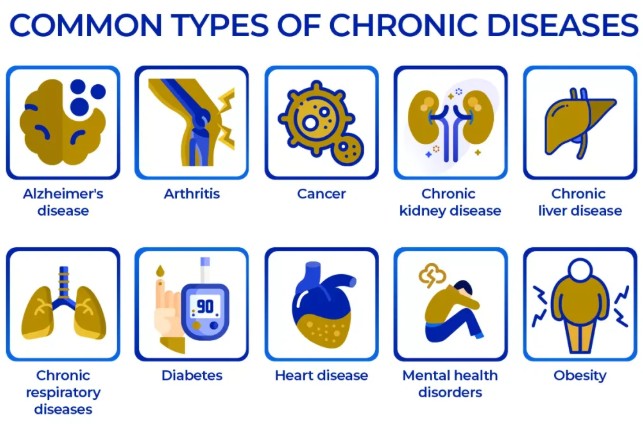
Chronic diseases continue to pose significant challenges to global health systems. As we approach 2025, the landscape of chronic disease management is evolving, and there are critical hurdles that healthcare professionals, policymakers, and society as a whole must address. This article explores some of the major challenges that are expected to shape the future of chronic disease care.
The Growing Burden of Chronic Diseases
The prevalence of chronic diseases is steadily increasing worldwide, placing unprecedented pressure on healthcare systems. Factors contributing to this growing burden include:
- Aging Population: As populations around the globe age, the incidence of age-related chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes, is expected to surge.
- Lifestyle Factors: Sedentary lifestyles, poor dietary choices, and increasing levels of stress contribute significantly to the development of chronic conditions.
- Environmental and Genetic Factors: Pollution, genetic predispositions, and other environmental factors are playing an increasing role in chronic disease prevalence.
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that by 2025, nearly three-quarters of the world’s population will be living with at least one chronic illness. This statistic underscores the urgent need for innovative approaches to chronic disease management.
Technological Advancements in Chronic Disease Management
The role of technology in managing chronic diseases cannot be overstated. From telemedicine to wearable health monitors, technology is reshaping how chronic conditions are diagnosed, monitored, and treated. Key technological advancements include:
Telehealth Services
Telehealth is breaking down geographical barriers to access healthcare and providing patients with remote consultation options. This is particularly beneficial for individuals managing chronic diseases who require frequent medical consultations.
- Improved Accessibility: Patients in rural or underserved areas can connect with healthcare providers without the need to travel long distances.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduced need for physical infrastructure and resources translates to lower healthcare costs for both providers and patients.
Wearable Technology and Health Apps
Wearables and health apps are empowering patients to take control of their health by providing them with real-time data and insights.
- Continuous Monitoring: Devices such as smartwatches and fitness trackers monitor vitals, enabling early detection and timely interventions.
- Personalized Healthcare: Data collected from wearables can be used to tailor treatment plans to individual patient needs.
Policy and Regulation Challenges
While technology offers promising solutions, the regulatory landscape presents significant hurdles. Ensuring patient privacy and data security is paramount, yet complex regulatory frameworks can stifle innovation. Key policy challenges to consider include:
Data Protection and Privacy
The collection and use of personal health data necessitate stringent privacy regulations. Healthcare providers must navigate regulations to protect patient data without hindering the integration of technological advancements.
- Ensuring Compliance: Navigating regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is crucial for healthcare organizations.
- Building Trust: Establishing trust with patients regarding data use is essential for widespread adoption of technology-based interventions.
Healthcare Policy Reform
Governments and policymakers must adopt forward-thinking reforms to address inefficiencies in healthcare systems and improve chronic disease outcomes.
- Resource Allocation: Prioritizing funding and resources for preventive care and chronic disease management initiatives.
- Collaborative Efforts: Encouraging partnerships between public and private sectors to drive innovation and improve access to care.
The Role of Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine is rapidly gaining traction as an approach to tailor medical treatment based on individual characteristics. This paradigm shift from a one-size-fits-all model to personalized care is expected to transform chronic disease management. Key aspects include:
Genomic Medicine
Genomic medicine involves analyzing an individual’s genetic makeup to guide treatment decisions.
- Targeted Therapies: Identifying genetic markers that predispose individuals to chronic diseases, allowing for targeted interventions.
- Risk Stratification: Predicting disease risk based on genetic factors and implementing preemptive care strategies.
Precision Nutrition
Precision nutrition involves customizing dietary recommendations based on an individual’s genomic, phenotypic, and lifestyle data.
- Dietary Interventions: Tailoring diets to manage chronic conditions more effectively.
- Metabolic Health: Optimizing nutrition to improve overall metabolic health and reduce chronic disease risk.
Public Awareness and Education
Public awareness and education are critical components in the fight against chronic diseases. Empowering individuals with knowledge and resources can significantly impact disease prevention and management. Key efforts include:
Health Promotion Campaigns
Effective health promotion campaigns can reach a broad audience and influence positive behavior change.
- Community Engagement: Initiatives that involve community participation and address local health concerns.
- Leveraging Technology: Utilizing social media platforms and digital tools to enhance campaign reach and engagement.
Patient Education
Educating patients about their conditions and treatment options is crucial for improving health outcomes.
- Self-Management: Teaching patients self-management skills to empower them in taking charge of their health.
- Informed Decision-Making: Providing patients with comprehensive information to make informed choices about their care.
In conclusion, the challenges surrounding chronic diseases are multifaceted and require a coordinated effort from various sectors. By embracing technological advancements, implementing effective policies, and fostering public awareness, we can address these challenges and improve the quality of life for those living with chronic conditions. As we move toward 2025, a proactive and forward-thinking approach is vital to mitigate the impact of chronic diseases on global health systems.