COVID Impacts Immune System, Leading to Long-Term Symptoms: Study
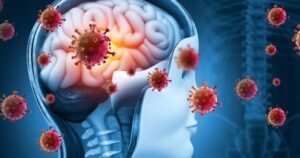
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has unearthed various health complexities, one being the lasting impact on the immune system. A recent study suggests that COVID-19 does more than just cause immediate illness; it can lead to long-term symptoms by profoundly affecting the immune system of those who contract it.
Understanding Long COVID
Long COVID, also known as post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), is a term used to describe a range of symptoms that persist for weeks or even months after the initial infection. Patients have reported a variety of lingering issues:
- Fatigue
- Brain fog
- Shortness of breath
- Muscle pain
- Persistent cough
- Loss of taste and smell
A comprehensive study conducted by researchers from a reputed institution has shed light on why these symptoms might persist and how COVID-19 impacts the immune system over the long haul.
Immune System and COVID-19
The immune system is our body’s natural defense against pathogens. When exposed to a virus like SARS-CoV-2, the immune system launches a multi-faceted response:
- Innate immunity: The first line of defense that responds immediately but non-specifically to pathogens.
- Adaptive immunity: A more targeted response that involves the production of antibodies to fight specific pathogens.
Immune Dysregulation
However, in the case of COVID-19, the virus can cause immune dysregulation, a situation where the immune system’s response becomes uncoordinated and sometimes harmful to the body itself. This dysregulation can lead to an overactive immune response, often termed a “cytokine storm,” which can cause damage to various organs and tissues.
The Study’s Key Findings
The recent study explored the mechanisms behind the long-term impacts of COVID-19 on the immune system. Here are some significant findings:
- T Cell Exhaustion: Prolonged COVID-19 infection can lead to the exhaustion of T cells, essential components of the immune system responsible for killing infected cells and supporting antibody production.
- B Cell Dysfunction: The study observed a decrease in the function of B cells, which produce antibodies to neutralize the virus. This dysfunction can impair the body’s ability to fend off not just COVID-19 but other infections as well.
- Chronic Inflammation: Persistent inflammation was a common finding among long COVID patients. Chronic inflammation can lead to other health issues, including autoimmune diseases and cardiovascular problems.
Impact on Different Populations
Age-Related Impacts
The study pointed out that older adults are more susceptible to long-term immune system damage caused by COVID-19:
- Pre-existing Conditions: Older individuals often have pre-existing health conditions such as diabetes and hypertension, making them more vulnerable to severe outcomes.
- Weaker Immune Response: Aging naturally weakens the immune system, which can exacerbate the effects of COVID-19.
Impact on Children
Although children generally experience milder symptoms, the implications of long COVID can still be significant:
- Multi-system Inflammatory Syndrome: Some children develop a condition known as Multi-system Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C), which can affect various organs, including the heart, lungs, kidneys, brain, skin, and gastrointestinal organs.
- Developmental Concerns: Prolonged illness in childhood can impact developmental milestones and overall growth.
Long COVID Management Strategies
Medical Interventions
Managing long COVID symptoms requires a multi-disciplinary approach:
- Medication: Anti-inflammatory drugs, antivirals, and immune modulators can be used to manage symptoms.
- Rehabilitation: Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and cognitive rehabilitation can help improve the quality of life for long COVID patients.
Lifestyle Adjustments
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle adjustments can play a crucial role:
- Balanced Diet: Nutrient-rich foods can support immune health.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can help reduce fatigue and improve overall well-being.
- Mental Health Support: Counseling and mental health support are crucial for dealing with the psychological impact of long-term illness.
Future Research Directions
The battle against COVID-19 is far from over, and understanding its long-term impacts is crucial for developing effective treatments. Future research is directed towards:
- Biomarker Identification: Identifying biomarkers that can predict who is at risk of developing long COVID symptoms.
- Vaccination Efficacy: Examining whether vaccinated individuals are less likely to experience long-term immune system damage.
- New Therapeutics: Developing new medications that can specifically target the long-term effects of the virus on the immune system.
The study highlights the profound impact COVID-19 can have on the immune system, leading to long-term symptoms that extend well beyond the acute phase of the illness. Awareness and ongoing research are essential in tackling this multifaceted health challenge.